Stop suffering and living in pain due to aching muscles. Knowing why your muscles ache will help you seek help before the muscle pain becomes crippling.
yourfootpalace.com gathered information on common reasons your muscles ache and how to make the pain and discomfort go away.
What is Muscle Pain
Muscle pain, or myalgia, is a sign, or result of an injury, infection, disease or other health problem. You may feel a deep, steady ache or random sharp pains. Some people can experience muscle pain all over, while others have it in specific areas. Everyone experiences and copes with muscle pain differently. Consider the following:
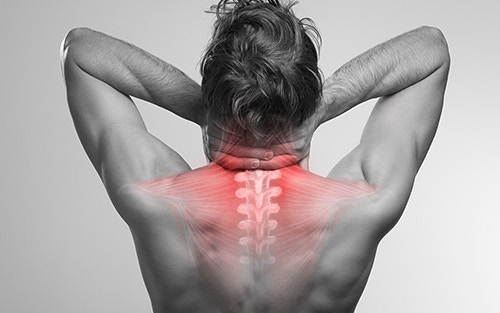
Back Pain (Dorsopathy)
Back pain can range from a single muscle aching to a severe shooting, burning, or stabbing sensation. The pain may radiate down your leg or worsen with bending, twisting, lifting, standing, or walking.
Potential Causes – Back pain can have causes that are not due to any underlying or preexisting disease or condition. Examples include overuse like working out or lifting too much, prolonged sitting, sleeping in an uncomfortable or cramped position, or wearing a poorly fitting backpack.
Treatment – Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, and others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve), can help relieve back pain. Take these over-the-counter medications only when directed or prescribed by your doctor. Overuse can cause serious side effects.
When to Seek Help – If your back pain lasts more than two weeks and keeps you from participating in normal, routine activities, see your primary care physician. If your pain is severe, you should see your doctor sooner. You should seek urgent/emergency medical care if you have a fever or chest pains associated with your back pain.
Prevention – Combine exercise (walking or swimming) with specific exercises to keep your back and abdomen core muscles strong and flexible. Strengthening your core muscles will help support your spine and can help prevent back pain. Proper lifting techniques, good posture, and frequent massages can also help prevent back pain.
Neck Pain (Cervicalgia)

People often describe this as having a stiff neck. Cervicalgia is any localized neck pain not radiating to other parts of the body. This is a common condition, as about two-thirds of all people will experience neck pain at some point in their lives.
Potential Causes – Common causes may include osteoarthritis, spinal stenosis, a herniated disc, a pinched nerve, mental and physical stress and strain, poor posture, tumors, poor sleeping position, and other health conditions.
Treatment – Alternating an ice pack with a heating pad several times for 30 minutes, gentle stretching, and massage can help relieve neck pain. Taking an over-the-counter pain medication like ibuprofen, acetaminophen, or naproxen may also help.
When to Seek Help – Seek immediate/emergency medical care if your neck pain is accompanied by numbness or weakness in your arms or hands or if you have shooting pain in your shoulders or down your arms.
Prevention – Get up and move around every half-hour. Prolonged sitting has been linked to worsening neck pain. When using your phone, a headset, earbuds, or speakerphone are excellent options to keep your head in a neutral position. And when reading a book, hold it, so you don’t have to lean down or forward to read it.
Elbow Pain (lateral epicondylitis)

Often called tennis elbow, this is a painful condition occurring when tendons in your elbow are overloaded or overextended, usually from repetitive wrist and arm motions. Despite the name, athletes aren’t the only people who can develop tennis elbow.
Potential Causes – A common cause of elbow pain is the inflammation of one or both of the elbow’s tendons. This is called tendonitis, and it often results from overuse. Repetitive movements from work, household chores, golf, or tennis can affect the muscles above and below the elbow and cause tendonitis.
Treatment – Applying an ice pack several times for 15 minutes, rest, compression, elevation, and massage can help relieve neck pain. Taking an over-the-counter pain medication like ibuprofen, acetaminophen, or naproxen may also help.
When to Seek Help – Seek emergency care if you detect a deformity or protruding bone in your elbow, and immediately call your doctor if you experience severe pain, trouble moving your elbow, turning your arm from palm up to palm down and vice versa, and swelling or bruising around the joint.
Prevention – Warm up properly and gently stretch your arm muscles before any physical activities or playing a sport involving repetitive arm movements. Avoid putting extra strain on your tendons.
Foot Pain (Plantar fasciitis)
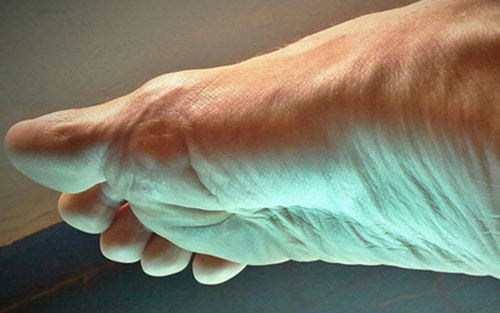
Plantar fasciitis (a common cause of heel and foot pain) is an inflammation of the fibrous tissue (plantar fascia) along the bottom of your foot, connecting your heel bone to your toes. This condition can cause intense, debilitating heel pain.
Potential Causes – Plantar fasciitis and foot pain, in general, can occur from arthritis, Injury, overuse, or conditions causing inflammation involving any of the bones, ligaments, or tendons in the foot.
Treatment – Rest your affected foot as much as possible, avoiding activities that worsen pain, and icing the affected area for up to 20 minutes multiple times daily may help relieve the pain. Taking an over-the-counter pain medication such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen may also help. Regular foot massages can also help accelerate your foot’s recovery.
When to Seek Help – Seek immediate medical care if you have an open wound or deformity, you experience severe pain or swelling, you can’t bear any weight on your foot, or it is showing signs of infection, like redness or fever.
Prevention – Most foot pain can be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding high-heel shoes, wearing shoes that fit, getting regular foot massages and pedicures, and keeping yourself well-hydrated.
Preventing, treating, and relieving plantar fasciitis pain is possible, so follow the above info and end your discomfort and nagging pain.
Muscle Pain
In this article, you discovered essential information about common reasons you may experience muscle pain, how to treat it, and when to seek medical attention.
Knowing what to do when you have muscle pain will help you recover more quickly and return to your normal activities.
Ignoring your muscle pain can lead to severe injuries, immobility, and even hospitalization if left undiagnosed and untreated.
Disclaimer: No content on this publication, page, or site, regardless of date or topic, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your primary care physician or other qualified clinician.
Sources:
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/17669-muscle-pain
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20369906
health.harvard.edu/pain/3-tips-to-prevent-neck-pain
hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/foot-pain-and-problems
(706) 521-5290
(678) 963-5958